Botonical Name | : | Curcuma Longa L | |
CAS # | : | 8024-37-1 | |
Country of Origin | : | India | |
Color & Odor | : | Pale yellow to reddish-brown oily liquid with Characteristic warm, spicy turmeric odor. | |
Solubility | : | soluble in oil & water | |
Specific Gravity | : | 0.925 – 0.935 @ 20°C | |
Optical Rotation | : | (-24) to (-27) @ 20°C | |
Refractive Index | : | 1.500 – 1.650 @ 20°C | |
Flash Point | : | 60 °C | |
Plant Part Used | : | Dry Root | |
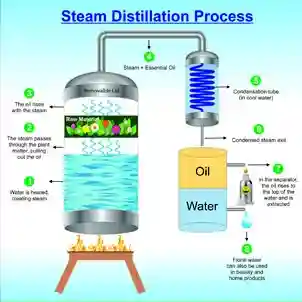
Extraction Method | : | Steam distillation |
DESCRIPTION:
Curcumin with concentration strength of 8.5% is a solvent extract of turmeric rhizome. Apart from colorant, it also acts as an antioxidant and has typical turmeric like odour. Also known by the name of Indian Saffron, it is used in a wide variety of ways in Indian cooking. The turmeric roots are pulled from the ground and separated from the rest of the plant and dried. The dried rhizome is ground and curcumin is extracted using a solvent. It is also very important herb and is widely recognized in Indian Ayurvedic medicine, as a spice and as a natural food colour. Further, turmeric is also seen as an excellent natural antibiotic. CONSTITUENTS:
Curcumin (yellow pigment) essential oil (artumerone, zingberene, borneol), alkaloids, valepotriates and protein. AROMATIC SUMMARY / NOTE / STRENGTH OF AROMA:
Characteristic Curcumin odor. BLENDS WITH:
Turmeric and curry powders. COMMON NAMES:
Indian Saffron. USES:
It finds application in the beverages, sauces and confectionery industry. Curcumin as an ancient Indian spice, is traditionally been used as medicine, condiment and flavouring agent. As per Indian Ayurvedic text, Curcumin extract also helps in improving body immunity, inducing the flow of bile, which breaks down fats. It also acts as an anti-inflammatory agent that helps in relieving aches & pains associated with arthritis.