Botonical Name | : | Alpina Officinalis/Galangal | |
CAS # | : | 8024-40-6 | |
Country of Origin | : | India | |
Color & Odor | : | Pale yellow to brown liquid | |
Solubility | : | Insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol and oils. | |
Specific Gravity | : | 0.9130 - 0.9230 @ 20 °C | |
Optical Rotation | : | --3.50 to -6.50 | |
Refractive Index | : | 1.4770 - 1.4810 @ 20 °C | |
Flash Point | : | >100°C | |
Major Constituents | : | Ethyl cinnamate , Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate , P-methoxycinnamic, galanga rhizome | |
Plant Part Used | : | Root | |
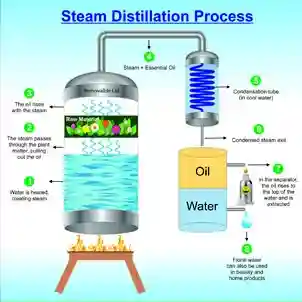
Extraction Method | : | Steam Distillation |
DESCRIPTION:
Raised in South West part of India and Eastern Himalayan regions, galangal is the dried root form of a specific medicinal plant. Olive brown or yellowish colored Galangal Oil is obtained from the fragmented and dried rhizomes of this herbal plant via steam distillation method. Apart from its application in pharmaceutical arena, it is also added in food as spice. CONSTITUENTS:
Ethyl cinnamate , Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate , P-methoxycinnamic acid. galanga rhizome. AROMATIC SUMMARY / NOTE / STRENGTH OF AROMA:
This essential oil has distinctive spicy smell and it also tastes like spice. BLENDS WITH:
This fragrant oil mixes with Ylang ylang essential oil.COMMON NAMES:
Galangal Essential Oil si commonly referred as False ginger Oil and Low-John Root oil. USES:
Apart from its usage as spice in culinary field, Galangal oil is also used to formulate medicines for treating bronchial catarrh, respiratory complications and rheumatism.